DESS® Dental | Study and Development of Ti-Bases

Ti-Bases Development | From inception to present day
Over the years, the various dental abutments manufacturers have launched their line of bases for zirconia structures.
Most of these abutments have been adapting according to the market trend in terms of development, which means that the vast majority have a similar, and sometimes almost identical, design.
Ti-Bases | Design Trends
As with most clinical and, in our case, dental solutions, technological advances have allowed for transformations and improvements in Ti-Base design over the years.
Keys to Optimal Cementation Retention
One of the milestones in the dental sector, and more specifically in implant dentistry, has been, since its inception, to improve the Ti-Base-crown cementation retention in order to achieve greater longevity of the prosthesis as a whole and thus improve the patient's quality of life.
Consequently, there are various attributes and aspects of Ti-Base design that contribute to improved cementation retention.
Read on to discover them!
Cementation Retention | Parallel Walls
The cementing surface of the Ti-Bases initially started from a conical design and later evolved to parallel walls. This is because several scientific studies* have shown that conical walls significantly decrease cement retention in zirconia restorations, increasing the risk of decementation.
The more height, the more retention?
Logic might lead us to believe that the higher the cementation height of the Ti-Base, the higher the retention of the final restoration, and the more cement the better, but it has been shown in several studies* that a cementation surface of more than 30mm2 does not represent a significant improvement in cement retention in parallel-walled components.
Surface Sandblasting | Improved retention
An additional method of optimising the Ti-Base's cement retention is the process of surface sandblasting. This procedure creates a textured surface favourable for more effective cement bonding, significantly reducing the risk of de-cementation.
Normally, the sandblasting process is applied to the abutment manually in the laboratory, where the zirconia is finalised, but at DESS®, the sandblasting treatment is applied to the abutments during the manufacturing process.
DESS® Ti-Bases | Optimal Retention
DESS® line of straight and angulated channel abutments has been developed taking into account all the above techniques for cementation retention enhancement, which are supported by various clinical trials and studies.
All DESS® Ti-Bases have been designed with the most innovative features, applying improvements to the techniques described in the previous sections. This has enabled DESS® Ti-Bases to achieve optimum cementation retention results.
Parallel walls
All interfaces have parallel walls, which increases cement adhesion, reducing the risk of decementation.
Optimal cementing surface
DESS® Ti-Bases cementing surface is higher than 30mm2, the minimum height to ensure adhesion.
SelectGrip® | 500% more bonding retention
DESS® Dental has applied SelectGrip®, a patented precision sandblasting treatment applied during the manufacturing process, which increases cement adhesion by up to 5 times compared to hand sandblasting in a laboratory, resulting in a homogeneous surface on every component.
In addition, the SelectGrip® Surface preserves a clean gingival area, a result that is almost impossible to achieve in a manual laboratory sandblasting process.
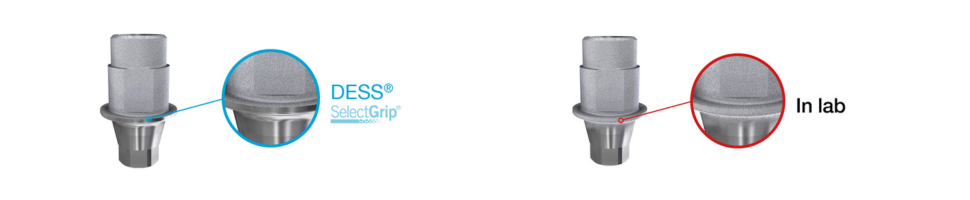
SelectGrip® | Flawless Surface
The patented SelectGrip® surface treatment is proof of DESS® Dental's innovation and understanding of the prosthetic process.
Sandblasting the Ti-Base surface is an essential process for the bonding of zirconia, without this process, de-cementation is an inevitable result.
One of the added values of DESS® products, which sets them apart from the rest of the products on the market, is that they are the only ones which are sandblasted at the production stage - no other interphase on the market is treated at this stage, which means that the dental professional has to process these components themselves. This involves a number of risks:
- The sandblasted surface result will not be completely homogeneous over the entire cementation surface.
- Critical areas such as the gingival area can easily be damaged, which will require a replacement component and the discarding of the damaged one.
SelectGrip® Surface | Benefits
Since 2009, DESS® Dental has been applying the SelectGrip® treatment on all its interfaces, which brings numerous benefits. 5x more retention compared to manual sandblasting procedure performed in the laboratory.
- Ensures that critical areas are intact and that the treatment is applied only on the surface where the restoration is to be cemented.
- Saves time for the user as it is not necessary to sandblast again.
- Ensures a homogeneous sandblasted surface throughout the component, a result that is practically impossible to achieve in a laboratory manual procedure.
- Adds extra value to the product without increasing the price.

DESS® Ti-Bases | Market Comparative Study
DESS® Ti-Base | Non-Angled Channel Abutments
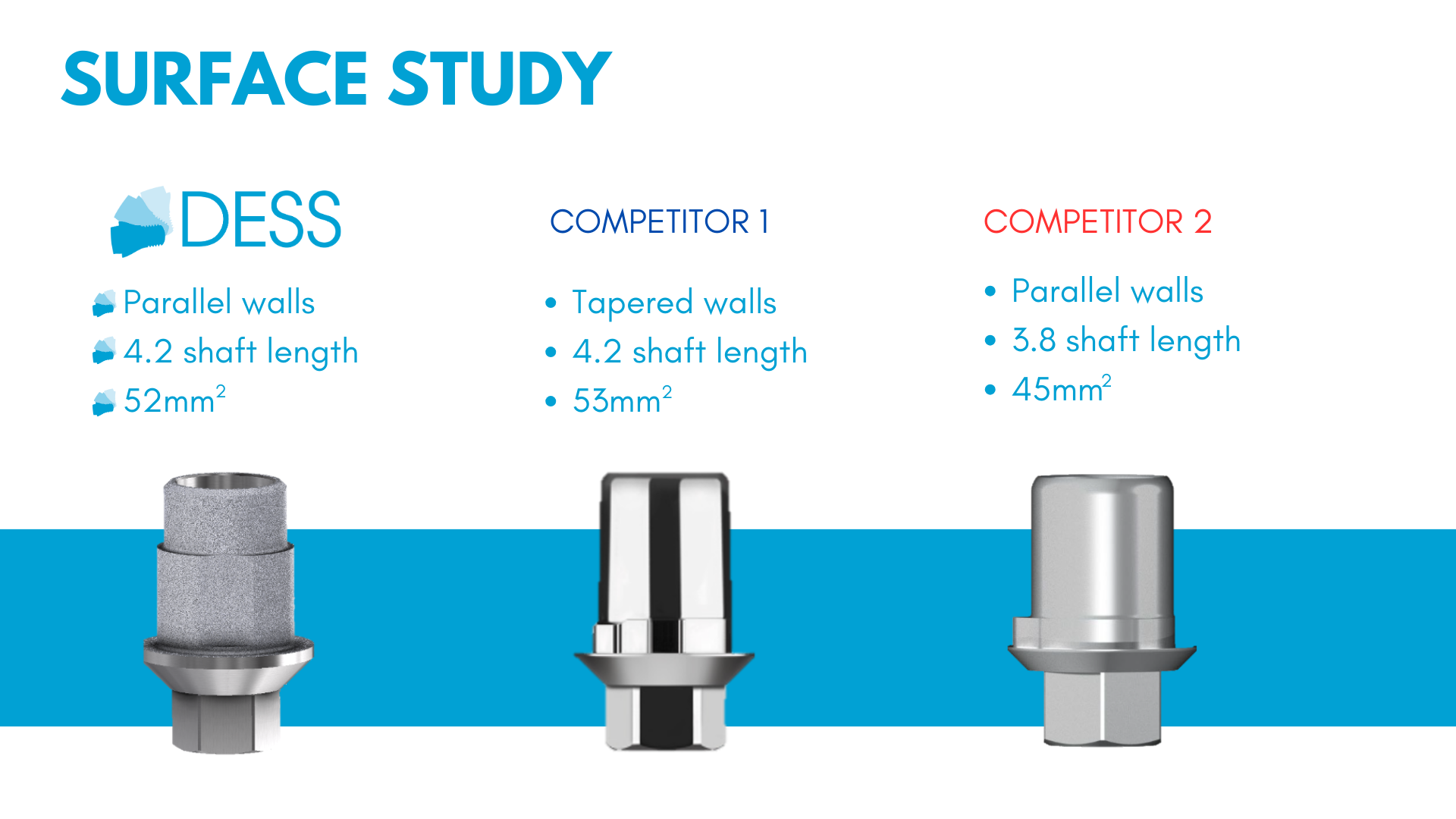
The DESS® Ti-Base is our straight channel titanium base, and has a surface area of 52mm2, making it one of the solutions with the largest cementation surface area.
Based on the many studies available, DESS® Ti-Base has been designed with parallel walls to ensure the highest cement adhesion, reducing the risk of debonding of the reconstruction.
On top of that, DESS® Ti-Base has been treated with SelectGrip® Surface to make it the abutment with more bonding retention on the market.
DESS® ANGLEBase® | Angulated Screw Channel Abutments

A comparison of the Angulated Screw Channel (ASC) solutions on the market shows that all the Ti-Bases have the same parallel wall design to increase bonding retention on the surface and reduce the risk of decementation.
However, there is a notable difference in the design of DESS® ANGLEBase®, as it is the only ASC solution on the market that breaks the "open window" design feature, making it the only solution that allows angulating the screw insertion from any direction.
The choice of this design feature is not arbitrary and has proven to have multiple functions and benefits.
DESS® ANGLEBase® | The Most Flexible Angular Channel on the Market
DESS® ANGLEBase® is considered the most flexible angular channel Ti-Base on the market due to its unique design features:
- Its "no open window" walls do not limit screw insertion in only one direction, but rather offer freedom to position the channel in any direction up to 25°.
- Its short chimney design (only 3 millimetres) favours a great aesthetic result and does not compromise the translucency of the zirconia compared to a titanium base with a higher height.
- The absence of a longer wall and the fact that it is completely cylindrical helps the component to distribute the forces evenly and work as a solid unit in conjunction with the restoration.
DESS® ANGLEBase® | The best surface
ANGLEBase® has a surface area of 40mm2 to ensure an angulation freedom of 25° in all directions. Its height, higher than the minimum recommended surface to ensure optimal cementation, does not compromise the cementation area. In addition, the SelectGrip® treatment ensures perfect bonding retention of the cement, eliminating any risk of decementation.
ANGLEBase® has been subjected to decementation tests comparing it to other existing solutions on the market.
The study compared an ANGLEBase® against a 4.5mm high titanium base. For a fairer comparison, the competitor's titanium base was sandblasted to create a similar surface to that obtained with SelectGrip®.
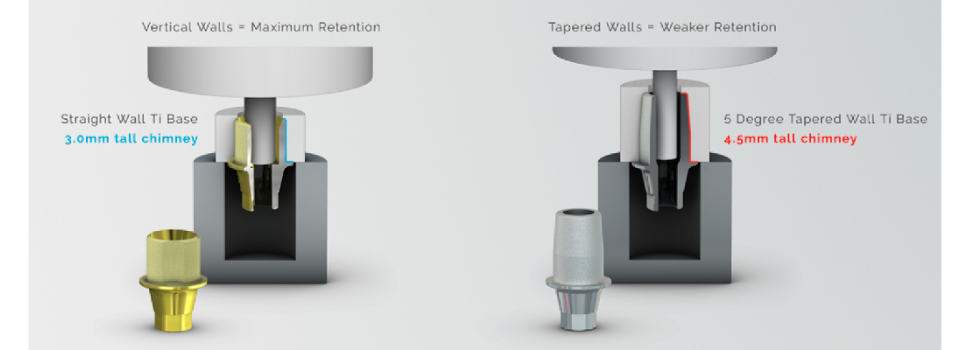
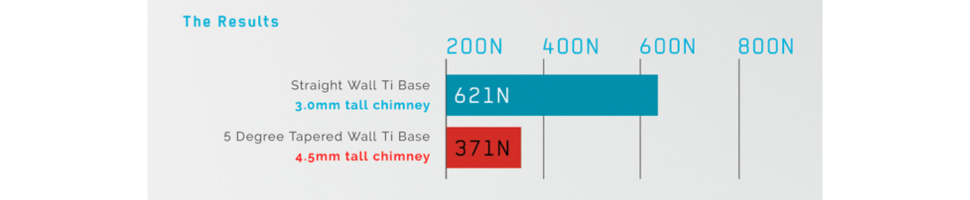
As a result, even though the competitor's titanium base is 50% longer, ANGLEBase® needs 621N to be debonded compared to the competitor's 371N.
It is easy to assume that a longer shaft should provide more retention; however, our testing and clinical experience clearly demonstrates that ANGLEBase® is a very safe and predictable product to use.
Without compromising cementation, it is the ultimate ASC solution since it allows the best aesthetic outcome, it gives an angular freedom of screw channel never seen on the market and it ensures the greatest flexibility in the production of the prosthetic restoration.